搜索结果: 1-15 共查到“生物学 pathogens”相关记录18条 . 查询时间(0.112 秒)
PLOS PATHOGENS|湖南农业大学水产学院李军华课题组揭示HSP90介导水生动物病毒病温度依赖性分子机理
PLOS PATHOGENS 李军华 HSP90 水生动物 病毒病 温度依赖性
2024/12/28
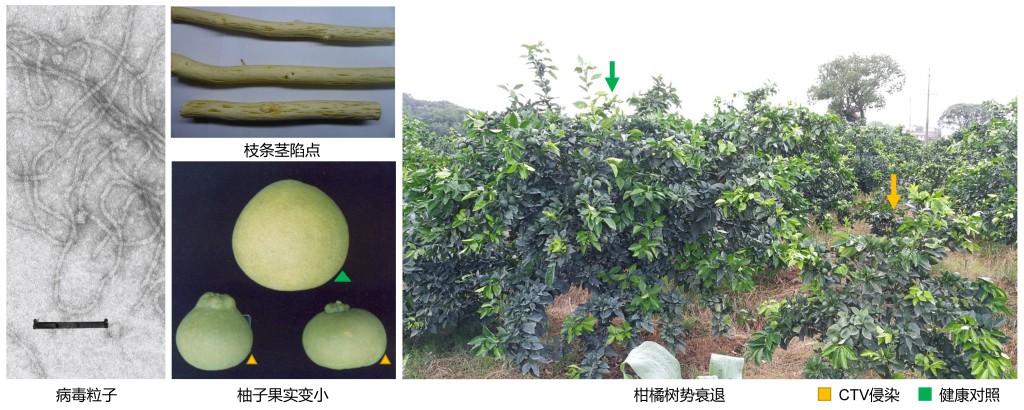

近日,国际病原学权威期刊PLoS Pathogens在线发表了来自西南大学柑桔研究所国家柑桔苗木脱毒中心周常勇/曹孟籍团队题为“Viromics unveils extraordinary genetic diversity of the family Closteroviridae in wild citrus”的研究论文。该研究利用宏病毒组学从野生柑橘中发现了4种长线形病毒,包括已知广泛分布的...

2021年3月1日,国际知名病原学期刊PLoS Pathogens在线发表了浙江大学农业与生物技术学院陈学新教授团队的最新研究成果“Symbiotic bracovirus of a parasite manipulates host lipid metabolism via tachykinin signaling”,揭示了寄生蜂调控寄主营养代谢的新机制,为天敌昆虫的高效繁育和害虫控制新技术的研...

近日,首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院杨国威研究员团队与中国医学科学院病原生物学研究所杨剑研究员团队合作在国际病原生物学期刊PLOS Pathogens同期发表了两篇题为Genome-wide dissection reveals diverse pathogenic roles of bacterial Tc toxins和N-Glycans and sulfated glycosaminoglyc...
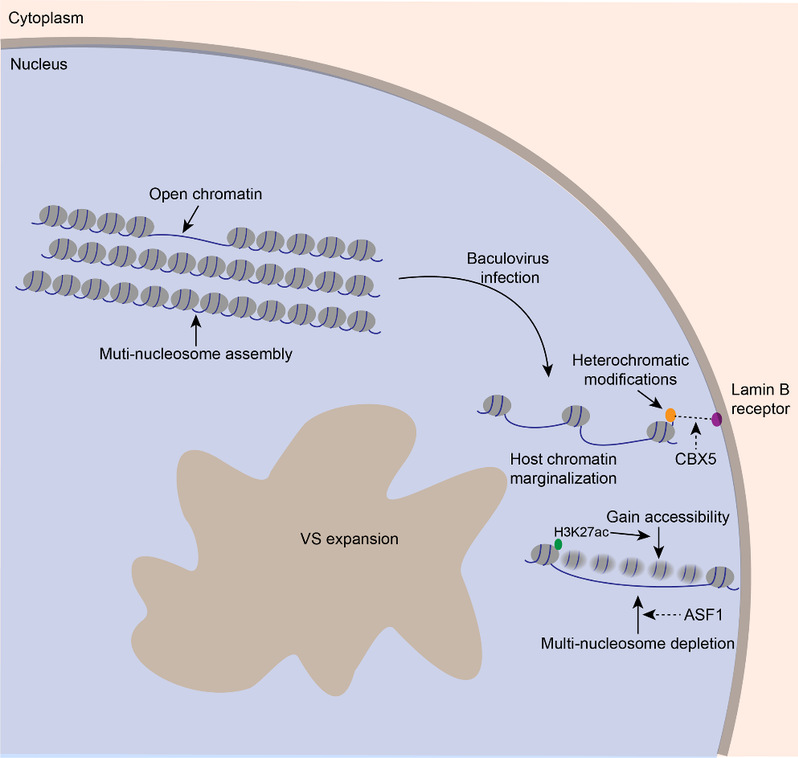
家蚕核型多角体病毒(BmNPV)是感染家蚕的主要病原,严重威胁蚕丝业生产。吴小锋教授课题组利用高通量测序手段(ATAC-seq,RNA-seq和ChIP-seq)、结合细胞与生化分析,揭示了BmNPV感染对家蚕宿主染色质状态的影响。BmNPV感染导致宿主染色质的边缘化,并在病毒感染的极晚期使宿主染色质处于更加开放的状态,并且核小体发生去组装现象,进一步发现组蛋白修饰参与了染色质状态的维持和变化。该...
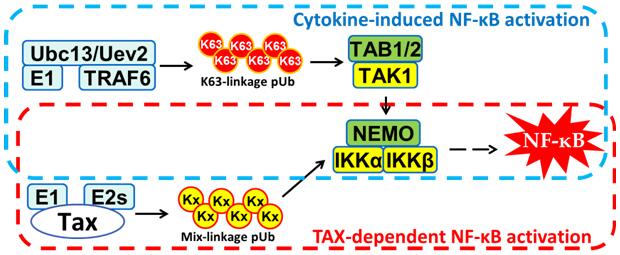
浙江大学生命科学研究院夏总平实验室在PLoS Pathogens发表论文揭示HTLV-1病毒蛋白Tax激活宿主NF-κB信号通路的机制(图)
浙江大学生命科学研究院夏总平实验室 PLoS Pathogens HTLV-1病毒蛋白Tax激活宿主NF-κB信号通路
2016/4/20
2016年4月15日,浙江大学生命科学研究院夏总平实验室在PLoS Pathogens刊物 (影响因子为7.562)上在线发表题为“HTLV-1 Tax Functions as a Ubiquitin E3 Ligase for Direct IKK Activation via Synthesis of Mixed-Linkage Polyubiquitin Chains”的研究论文。人T细胞...
Purdue innovation provides 'fingerprint' to identify foodborne pathogens,moves closer to production
Purdue fingerprint foodborne pathogens moves closer to production
2016/2/22
A Purdue University innovation that creates a "fingerprint-like pattern" to identify foodborne pathogens without using reagents has been licensed by Hettich Lab Technology. The technology is...
Antiviral compound may protect brain from pathogens, West Nile virus study shows
Antiviral compound pathogens West Nile virus
2015/5/25
Researchers have found that an antiviral compound may protect the brain from invading pathogens. Studying West Nile virus infection in mice, scientists at Washington University School of Med...
中国科学院动物研究所孙钦秒研究组有关抗DNA病毒天然免疫反应的研究进展在PLoS Pathogens发表
中国科学院动物研究所 孙钦秒研究组 抗DNA病毒天然免疫 PLoS Pathogens发表
2015/4/2
天然免疫系统是机体抵抗病原微生物入侵的第一道防线。STING作为细胞质内抗DNA病毒天然免疫反应的重要因子,通过N端的多个跨膜区定位于内质网上,它的定位对于其功能起着非常重要的作用。STING介导的免疫反应过强会导致一些炎症疾病,因此机体如何精确调控STING介导的免疫反应至关重要。孙钦秒研究组发现PPM1A以依赖磷酸酶活性方式负调控STING介导的信号。研究表明PPM1A可以与STING和TBK...

Testing for pathogens(图)
pathogens colleagues
2014/12/1
When Sunny Shah and his research colleagues at the University of Notre Dame developed a new diagnostic tool for detecting the presence of bacteria, viruses and other pathogens, they assumed that the f...
Experts advocate for stronger measures to protect trees and other plants from pests and pathogens
Experts advocate stronger measures protect trees other plants pests and pathogens
2013/5/27
As the fungus responsible for ash dieback continues to devastate ash tree populations throughout the UK and other threats to the countryside continue to emerge, experts convened by Defra are advocatin...
天然免疫系统是机体抵抗病原微生物入侵的第一道防线,它首先通过模式识别受体(PRRs)与病原体相关分子模式(PAMPs)相互识别,进一步激活一系列的免疫反应。同时,宿主细胞通过多种方式负调节天然免疫反应的信号通路,以保证信号传导的平衡,进而防止过度免疫反应对宿主细胞造成损伤。在抗RNA病毒天然免疫中,主要有两类PRRs: TLRs 和RLRs。 MAVS作为RLRs介导的抗病毒免疫信号通路中的重要接...
Inhibitory Activity of Garlic Fermented by Pediococcus pentosaceus KACC 91419 against Antibiotic-resistant Pathogens
Pediococcus pentosaceus KACC 91419 Garlic Fermentation Antibiotics Resistance
2016/5/5
The aim of this study was to screen lactic acid bacteria for the fermentation of garlic and to assess the increase in inhibitory activity of garlic fermented against antibiotic-resistant pathogens for...
Occurrence of the Pathogens and Parasites of Phyllotreta undulata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Turkey
Pathogen parasite Hexamermis microsporidium Phyllotreta undulata
2010/3/25
The pathogens and parasites of Pyllotreta undulata Kutschera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) collected from 5 localities in the Black Sea region of Turkey were investigated. Four different types of pathog...
Study takes aim at opportunistic fungal pathogens--Research provides genome sequences and critical analyses of key Candida species
fungal pathogens genome sequences critical analyses Candida species
2009/6/22
In what represents one of the largest comparative genomics studies to date, scientists have cracked the genetic code of several fungal species that cause bloodstream infections in patients with suppre...


